By: Team F11-1
Since: August 2019
Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. About
- 3. Quick Start
- 4. Parameter Constraints and Additional Information
- 5. Features
- 5.1. Saving the data:
- 5.2. Viewing help :
help - 5.3. Adding an Entity:
add {participant/mentor/team} - 5.4. Updating an Entity:
edit {mentor/participant/team} ENTITY_ID [PARAMETERS] - 5.5. Listing all Entities :
list {mentors/participants/teams} - 5.6. Viewing a Specific Entity:
view {mentor/participant/team} ID - 5.7. Deleting an Entity:
delete {mentor/participant/team} ID - 5.8. Finding a Specific Entity:
find {mentor/team/participant} n/NAME … - 5.9. Advanced Finding of a Specific Entity by Union or Negative:
find [AND/OR] {mentor/team/participant} n/NAME … [EXCLUDE] … - 5.10. Assigning a Entity to a Team:
assign {mentor/participant} ID TEAM_ID … - 5.11. Removing an Entity from a Team:
remove {mentor/participant} ID TEAM_ID … - 5.12. Show Command History:
history - 5.13. Undo Previous Commands:
undo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_UNDO] - 5.14. Redo Previous Commands:
redo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_REDO] - 5.15. Command History Navigation
- 5.16. Scoring:
score - 5.17. Team Rankings:
leaderboardandgetTop k - 5.18. Bulk Registration:
import fp/PATH_TO_CSV_FILE [fp/PATH_TO_ERROR_FILE] - 5.19. Export Data:
export [{mentor/participant/team}] [fp/DESIRED_CSV_FILE_PATH] - 5.20. Help command
- 5.21. Home command:
home - 5.22. Command Suggestion Prompt
- 5.23. Seating:
locate {PARTICIPANT/TEAM}(Coming in v2.0) - 5.24. Swag (Coming in v2.0)
- 5.25. Schedule (Coming in v2.0)
- 5.26. Food (Coming in v2.0)
- 5.27. Waitlist (Coming in v2.0)
- 6. FAQ
- 7. Command Summary
1. Introduction
Alfred is a desktop application to help Hackathons' Human Resource Managers organise a Hackathon event. Hackathons are difficult to manage manually as they involve different groups of individuals, each of whom have a different role to play and agenda to fulfill in the Hackathon. Alfred helps streamline this organisation and management process, allowing you to quickly get up to speed with the logistics and administrative details of the Hackathon you are organising.
Furthermore, Alfred is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI), while maintaining the benefits of having visual responses in a Graphical User Interface. This means that users mainly interact with Alfred by typing on the keyboard, instead of using the mouse to point and click. Point-and-click functionality is supported, but is not the main focus of the application.
Interested? Well, head to Section 3, “Quick Start” to get started. We hope Alfred serves you well!
2. About
This User Guide introduces you to Alfred’s features and how you can use them to enhance your productivity when organising a Hackathon. You can use Alfred to add and track participants in your Hackathon, assign mentors to participants, keep track of the scores of each team in a leaderboard, undo and redo changes you make, and a whole lot more. Note that Alfred was built for you to focus on and organise a single Hackathon event.
Alfred was designed to be as easy to use as possible, and the only assumption we made is that users are comfortable typing into a keyboard to interact with Alfred. No other technical knowledge is needed! It’s that simple.
Alfred is designed to be cross-platform and is available for the Linux, Windows and Mac OS operating systems.
Some simple conventions are used for this User Guide:
-
Commands - You will typically interact with Alfred through what we call "commands". Each command is simply some text that you enter into Alfred. The command text that you should enter at the command line is formatted as
user input
3. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
alfred.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for Alfred.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. Alternatively, if you use a Mac, type the command
java -jar alfred.jaror replacealfred.jarwith the name of the jar file downloaded. on terminal in the jar file’s directory to open and start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.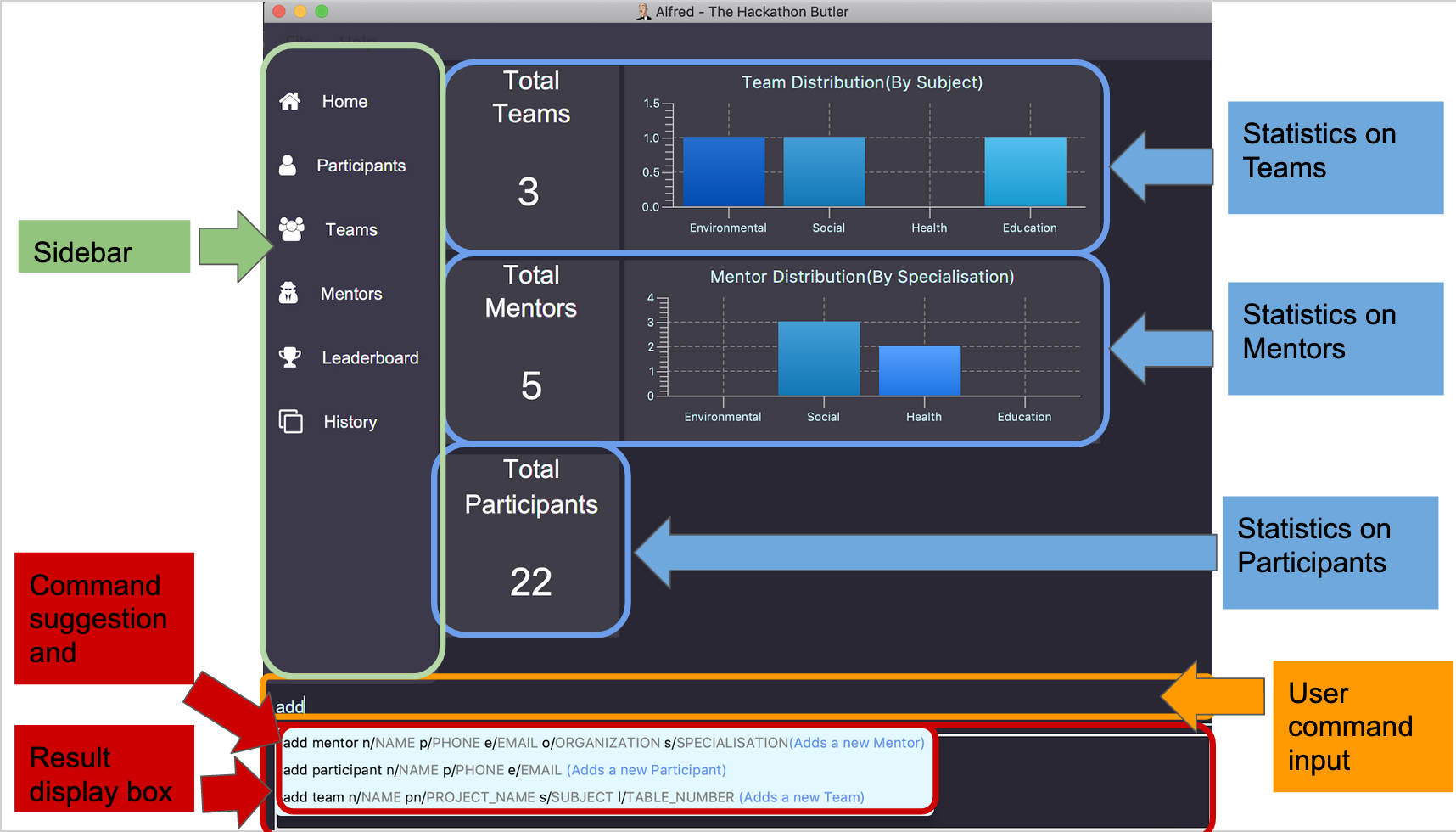 Figure 1. Layout of the application
Figure 1. Layout of the application -
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Here are some sample commands you can experiment with:
-
list teams: lists teams in the hackathon -
add participant n/Bartholomew Lim p/+6597654321 e/barrytheflash@superheros.com: adds a new participant namedBartholomew Limto the Hackathon. -
delete participant P-1: removes the participant with ID P-1 from the hackathon. -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 5, “Features” for details of each command.
5. Features
Prelude - Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters which you need to supply. For example, inadd mentor n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which you need to specify as the mentor’s name (i.e.add mentor n/John Doe). -
You can input the parameters in any order. For instance, if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER, you may inputp/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEand Alfred will still consider it as an acceptable command. -
Words in {curly braces} indicate values for the command that you need to select and provide.
-
For example in the case of
add {mentor/participant/list}, you can choose to typeadd mentor,add participantoradd team
-
-
Words in [brackets] indicate values that are optional for the command.
-
For example, in the case of
export [CSV_FILE_PATH], you can choose to leave out the file path.
-
-
Whenever you need to specify an ID, the ID will be prefixed with an alphabet indicating the type of the Entity (e.g. M for Mentors, P for Participants, T for Teams).
-
Type your commands in the textbox displayed on the Alfred UI. After you are done typing the command, press Enter on your keyboard to execute the command.
Also, please refer to Section 4, “Parameter Constraints and Additional Information” for more information on the different restrictions for each parameter.
5.1. Saving the data:
Data in Alfred is saved to the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need for you to save the data manually.
Should any tampering of the data in storage result in an invalid state for the data, the data will be re-initialised and the old data will be lost. Hence, please avoid directly altering the storage files as any minor errors could result in permanent loss of critical information.
5.2. Viewing help : help
If at anytime you don’t understand how to do a certain thing on Alfred, use this command to display a help page in a separate pop-up window.
To close the window, run any non-help command.
Format: help
5.3. Adding an Entity: add {participant/mentor/team}
Use this command to add a new entity for Alfred to keep track of.
5.3.1. Adding a Participant: add participant PARAMETERS
Use this command to add a new Participant to Alfred to keep track of for your hackathon.
Format: add participant n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL_ADDRESS
Examples:
-
add participant n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com -
add participant n/Betsy Crowe e/betsycrowe@example.com p/1234567
5.3.2. Adding a Mentor: add mentor PARAMETERS
Use this command to add a new Mentor to Alfred to keep track of for your Hackathon.
Format: add mentor n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL_ADDRESS o/ORGANIZATION s/SPECIALISATION
Examples:
-
add mentor n/Professor Superman p/91236549 e/clarkkent@gmail.com o/Daily Planet s/Social -
add mentor n/Doctor Batman p/91236549 e/bruce@gmail.com o/Google s/Environmental
5.3.3. Adding a Team: add team PARAMETERS
Use this command to add a new Team to Alfred to keep track of for your Hackathon.
Format: add team n/NAME s/SUBJECT pn/PROJECT_NAME l/TABLE_NUMBER
Examples:
-
add team n/Team01 s/Social pn/EmotionTrain l/12 -
add team n/HackathonWinners4Sure s/Environmental pn/Path-ify l/3
5.4. Updating an Entity: edit {mentor/participant/team} ENTITY_ID [PARAMETERS]
Edits an entity based on the parameter values you supply. Use this command in case you want to make changes to an entity you have already created within Alfred.
Examples:
-
edit mentor M-1 n/NewMentorName -
edit team T-1 n/NewTeamName pn/New Project Name -
edit participant P-1 n/NewParticipantNAme
5.5. Listing all Entities : list {mentors/participants/teams}
Shows a list of all the entities corresponding to the entity you specified that Alfred keeps track of.
Examples:
-
list mentorswill list all mentors stored within Alfred. -
list participantswill list all hackathon participants stored within Alfred. -
list teamswill list all hackathon teams stored within Alfred.
5.6. Viewing a Specific Entity: view {mentor/participant/team} ID
Shows a single entity with given ID.
Examples:
-
view mentor M-1will show the mentor with ID M-1 stored within Alfred. -
view participant P-1will show the hackathon participant with ID P-1 stored within Alfred. -
view team T-1will show the hackathon team with ID T-1 stored within Alfred.
5.7. Deleting an Entity: delete {mentor/participant/team} ID
Deletes an Entity, so that Alfred will no longer keep track of that Entity.
Examples:
-
delete mentor M-1will delete the mentor with ID M-1 from Alfred. -
delete participant P-1will delete the participant with ID P-1 from Alfred. -
delete team T-1will delete the team with ID T-1 from Alfred.
5.8. Finding a Specific Entity: find {mentor/team/participant} n/NAME …
Searches for Entities by selected fields, instead of their ID, in case you find that the ID is difficult to keep track of.
Examples:
-
find mentor n/Joshua Wongwill display a list of all mentors in the Hackathon who are named "Joshua Wong", or have "Joshua Wong" in their name. -
find participant n/John Doewill display a list of all participants in the Hackathon who are named "John Doe", or have "John Doe" in their name. -
find team n/FutureHackathonWinnerwill display a list of all teams in the Hackathon that are named "FutureHackathonWinner", or have "FutureHackathonWinner" in their name.
Each entity will have different fields available to find.
For participant, n/NAME e/EMAIL p/PHONE are all options to search for.
For team, n/TEAMNAME pn/PROJECTNAME are also all options to search for.
For mentor, n/NAME, e/EMAIL, p/PHONE o/ORGANIZATION are all available.
Example for multiple fields:
-
find participant n/Damith e/damith.comfinds all participants whose name contains the string "Damith" and whose email contains "damith.com"
5.9. Advanced Finding of a Specific Entity by Union or Negative: find [AND/OR] {mentor/team/participant} n/NAME … [EXCLUDE] …
The default find command for single and multiple fields works via a find by intersection. That is, entities
must be true for all the predicates for it to be displayed. However, Alfred also supports finding by union.
As above, all find commands are case insensitive.
The commands for this is as such:
-
find participant OR n/Damith e/nuswill do a search for all Participants whose name contains "Damith" or whose email contains "nus" in it.
Also do note that for this command, the OR key must be placed before all the arguments to the command. Also, the OR key can be replaced by the AND key to do a search by intersection. If none are provided, then a search by intersection is done by default. The AND/OR keyword must be in caps.
Next, Alfred also supports negative searches, if you wish to do it. Simply run
-
find mentor n/Boss EXCLUDE e/boss.comwill return all mentors whose name has a "boss" and whose email does not contain "boss.com"
Also, you can do negative searches by union as well.
-
find mentor OR n/boss EXCLUDE e/boss.comwill now return all mentors whose name has a "boss" in it or whose email does not contain "boss.com"
However, there are also some caveats when it comes to using find.
-
The
AND/ORkeyword must be placed at the front before all parameters and theEXCLUDEkeyword -
Anything after the
EXCLUDEkeyword will be processed using negative find. -
No
AND/ORkeywords are allowed after theEXCLUDEkeyword. -
You can only search by
ANDorOR. You cannot do a search by bothANDandOR
Other examples of valid commands are also provided here for your reference:
-
find team OR EXCLUDE n/ArsenalFC pn/Footballwill do a search of all teams whose name does not contain "ArsenalFC" or whose project name does not contain "Football". -
find participant AND n/Abramov EXCLUDE e/reactwill do a search where participant names contain "Abramov" and whose email does not contain "react". In this case, theANDkeyword could have been omitted because the default find does a search by intersection.
5.10. Assigning a Entity to a Team: assign {mentor/participant} ID TEAM_ID …
Assigns Mentor or Participant Entity by their ID to a team identified by TEAM_ID. It is possible to assign a participant or mentor to multiple teams.
Examples:
-
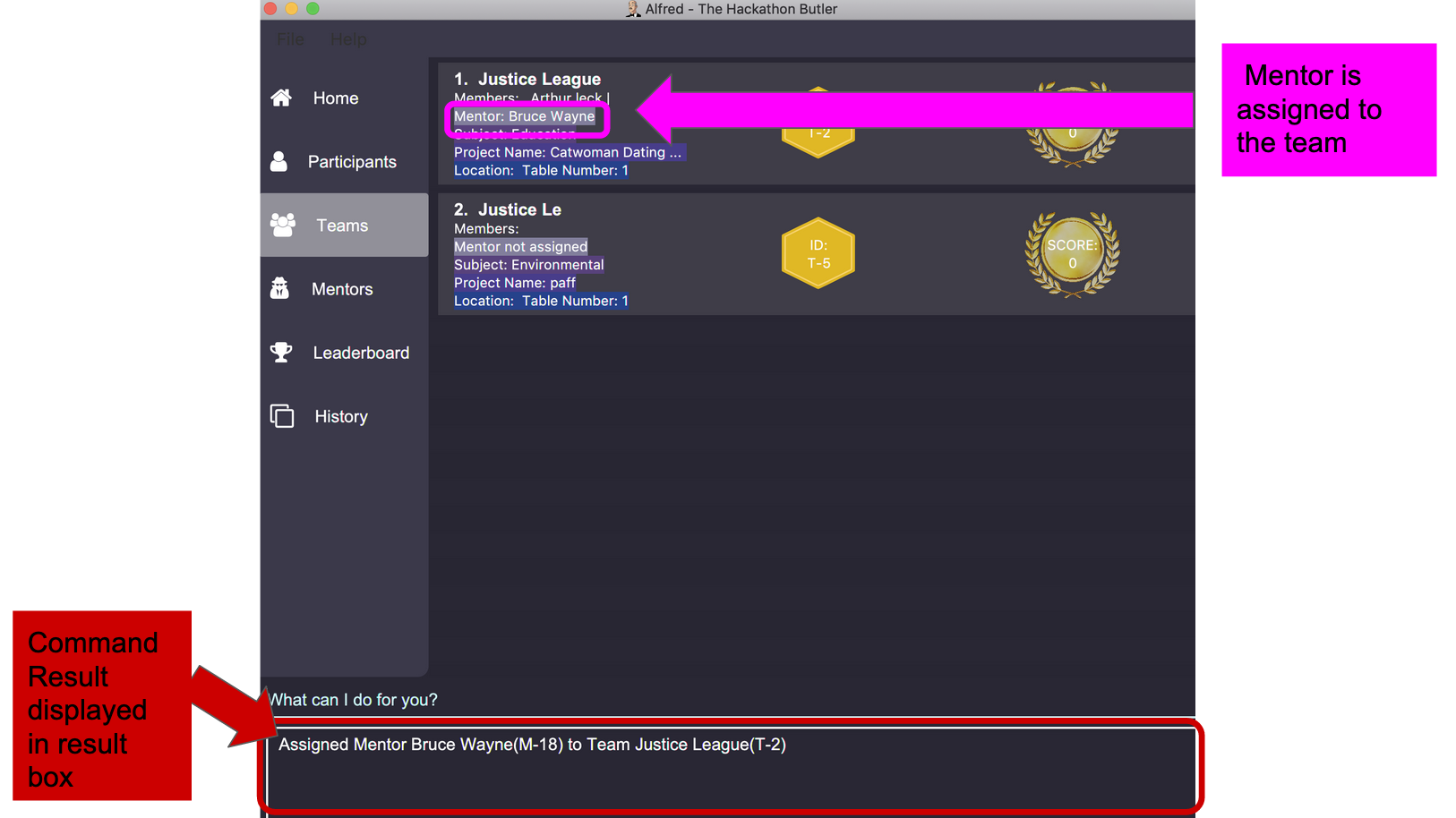
assign mentor M-18 T-2will assign a Mentor with ID M-18 to Team with ID T-2. Running the command will show you the following output in the 'Team' section of the GUI:
-
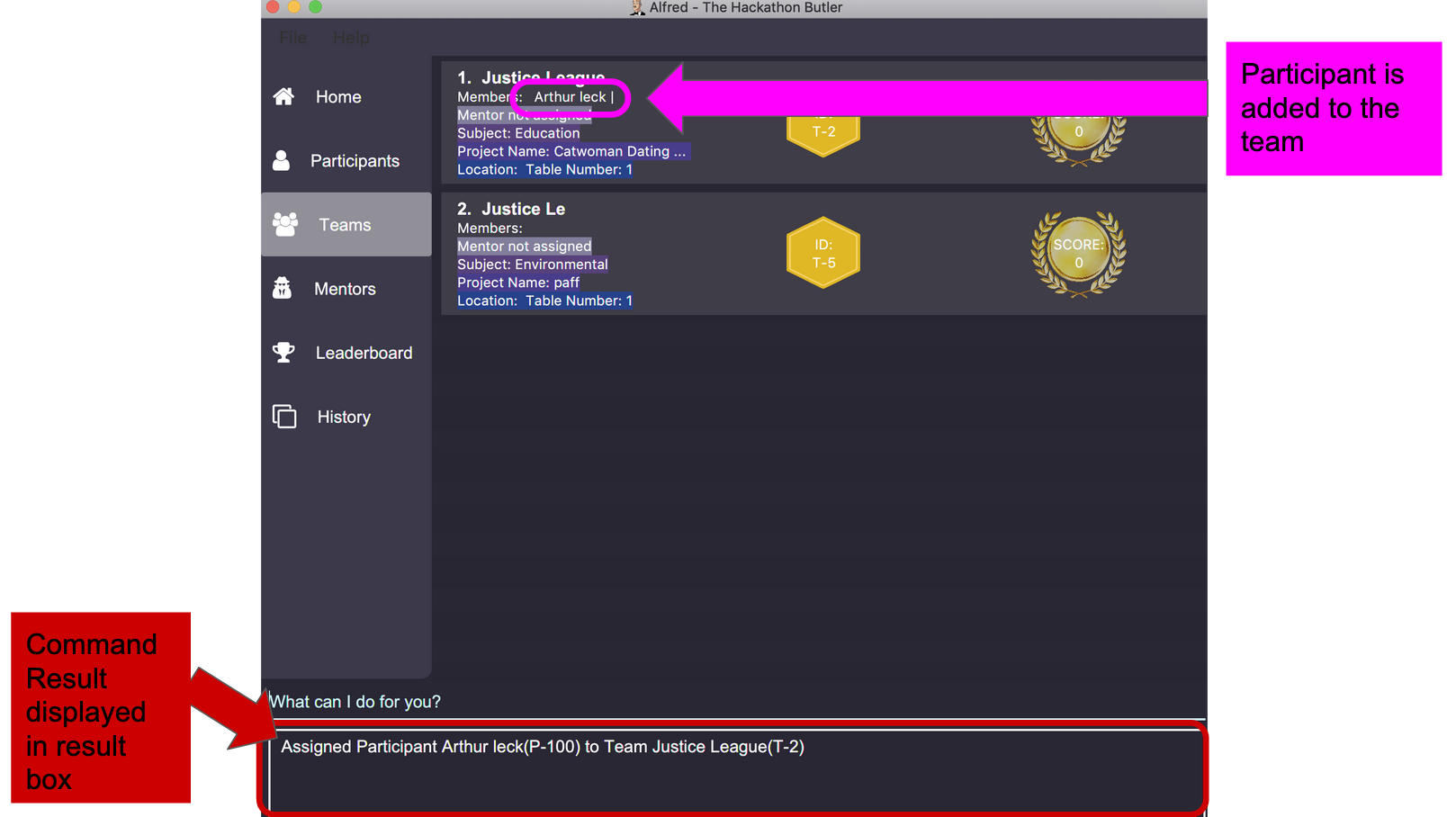
assign participant P-100 T-2will assign Participant with ID P-100 to Team with ID T-2. Running the command will show you the following output in the 'Team' section of the GUI:
5.11. Removing an Entity from a Team: remove {mentor/participant} ID TEAM_ID …
Removes Mentor or Participant Entity by their ID from a team identified by TEAM_ID.
Examples:
-
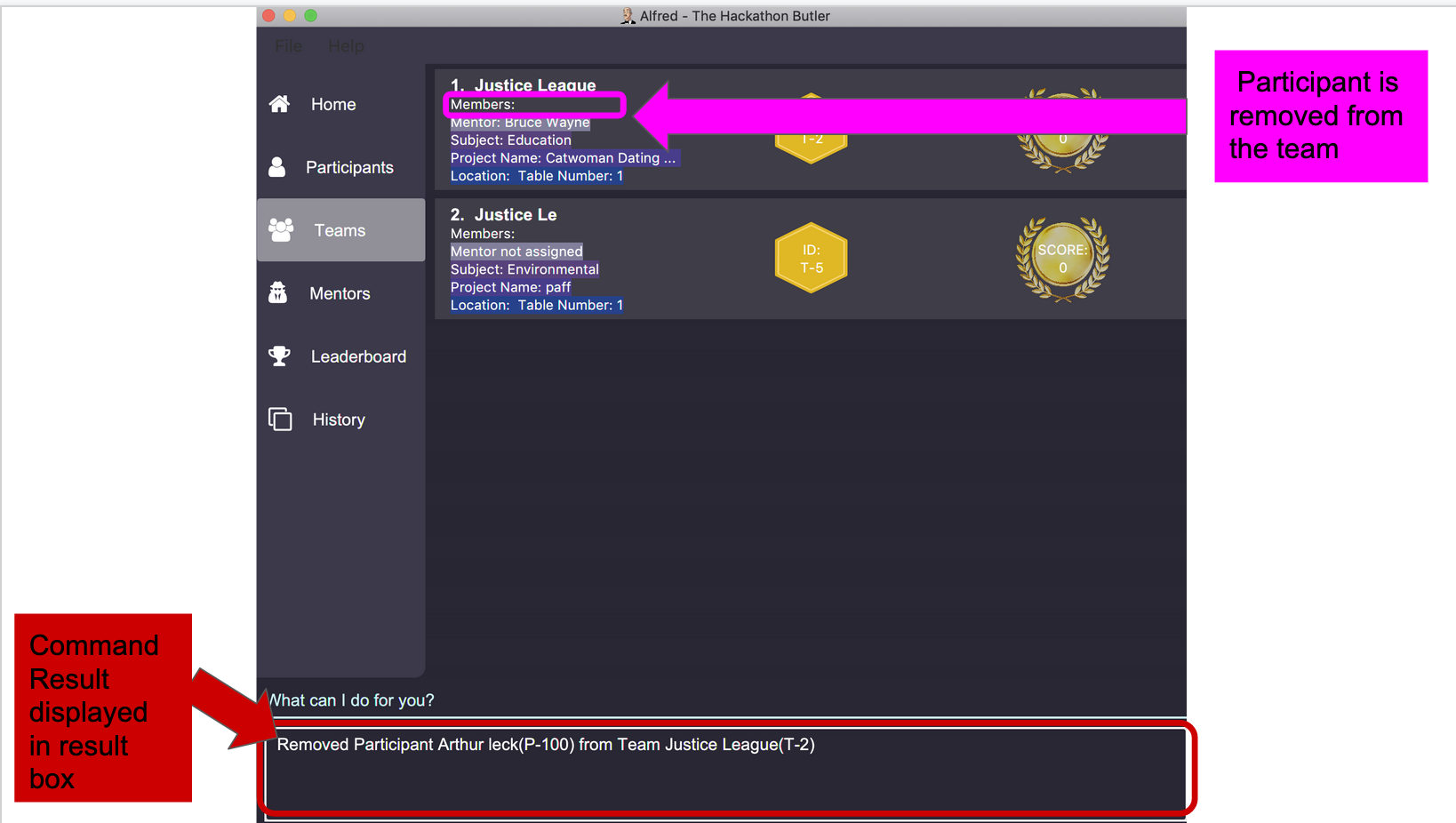
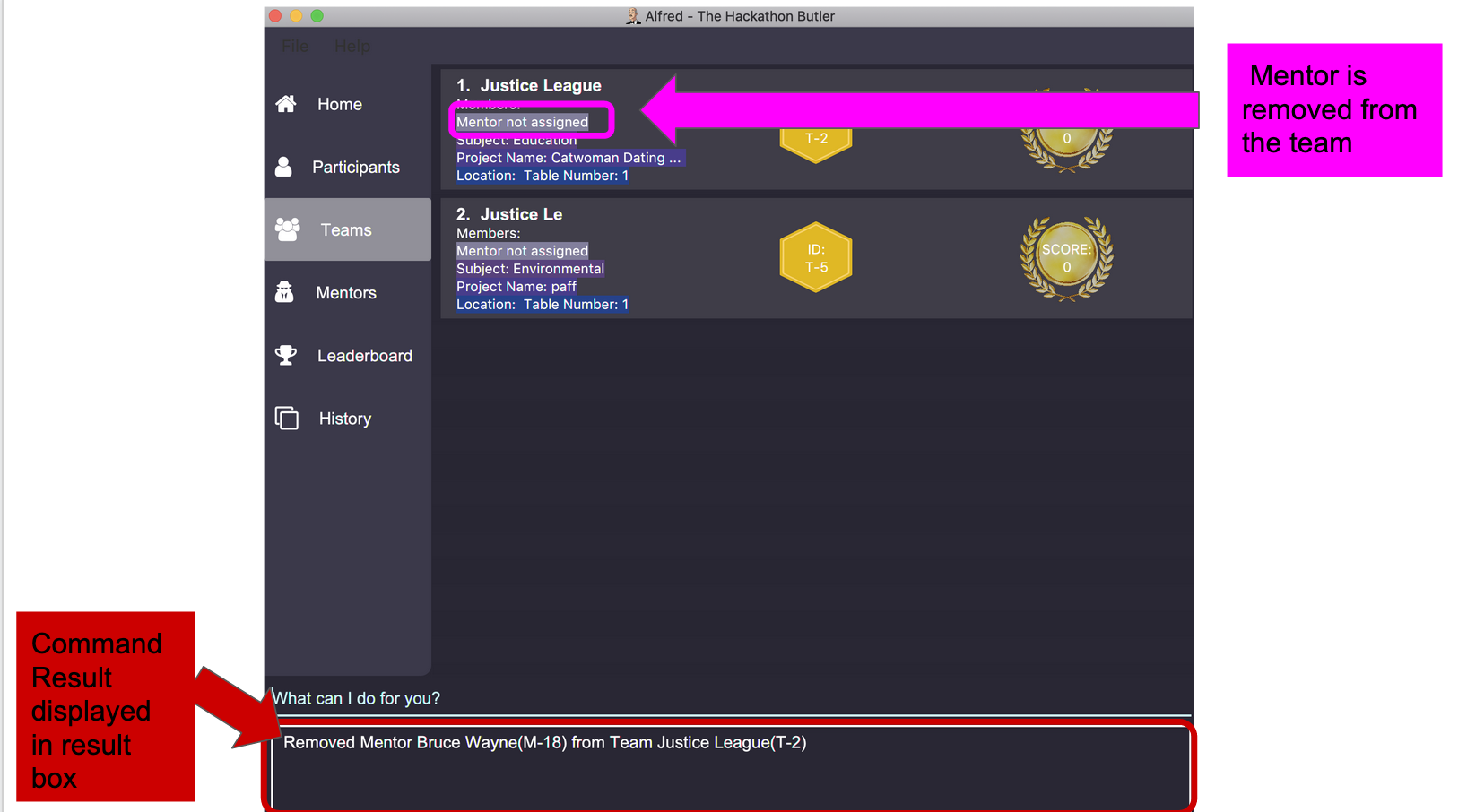
remove mentor M-18 T-8will remove Mentor with ID M-18 to Team with ID T-8. Running the command will show you the text 'Mentor not assigned' in the respective team. The following will be shown in the 'Team' section of the GUI:
-
remove participant P-100 T-2will remove Participant with ID P-100 from Team with ID T-2.Running the command will show you the following output in the 'Team' section of the GUI
5.12. Show Command History: history
Shows you up to the last 50 commands that you executed.
The following commands are not undo/redo-able: help, list, find, history, leaderboard, getTop, export, help, home, undo, redo.
All other commands are undo/redo-able.
|
Example:
After running the following commands:
-
list participants -
add participant n/SuperHero1 p/+6591111111 e/superhero1@gmail.com -
add participant n/SuperHero2 p/+6592222222 e/superhero2@gmail.com -
add participant n/SuperHero3 p/+6593333333 e/superhero3@gmail.com -
edit participant P-4 n/The Flash
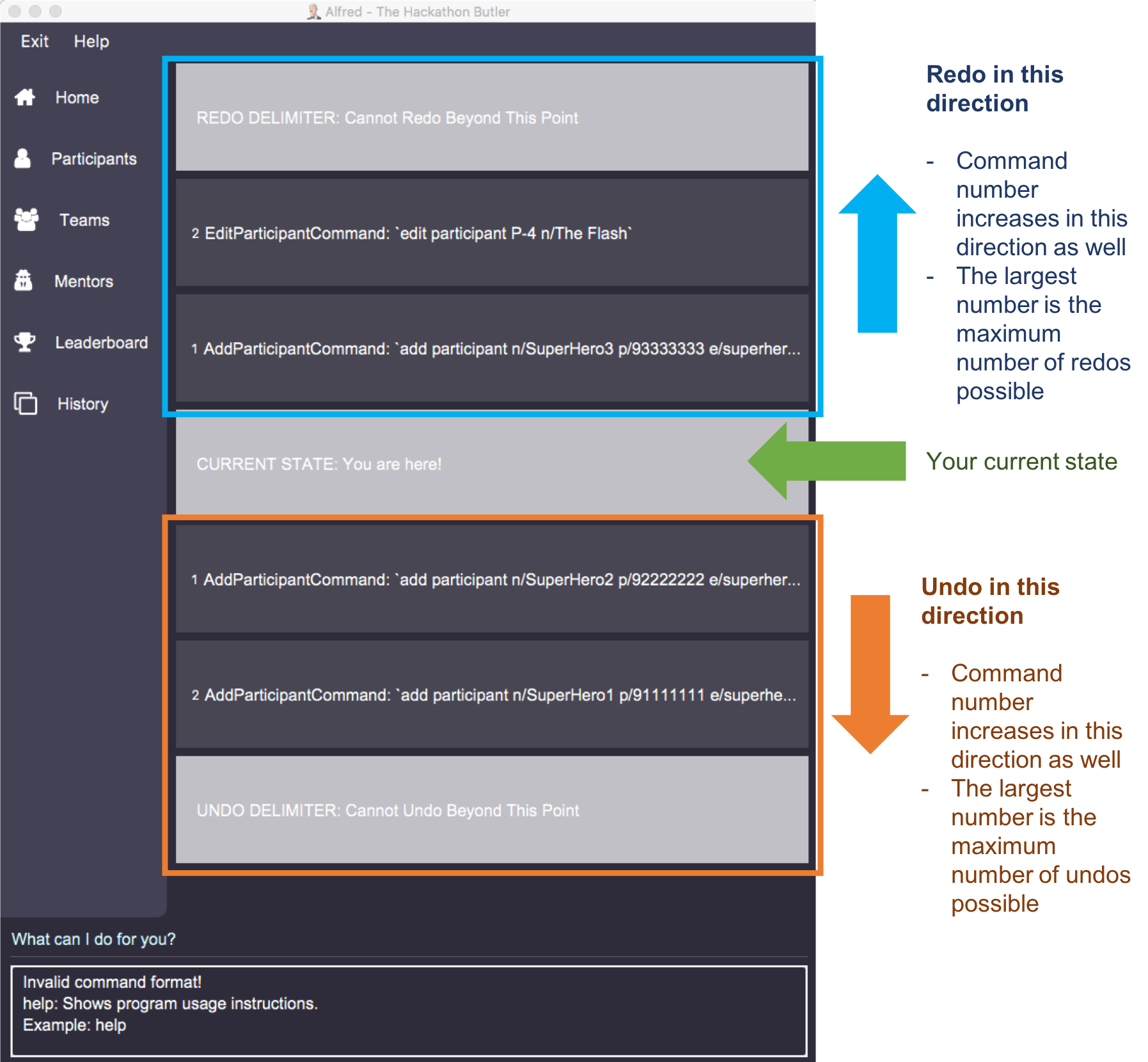
Running history will show you the following output in the "History" section of the Graphical User Interface:
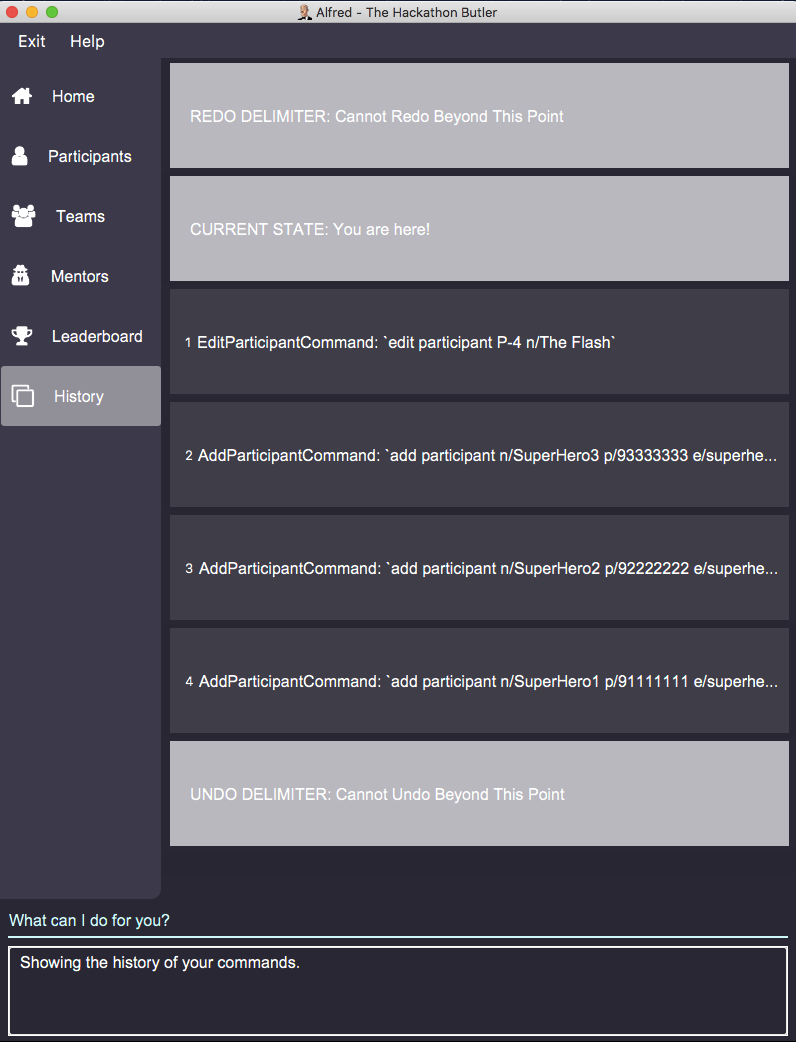
The topmost panel is the "redo" delimiter. The second panel from the top is the "current" delimiter. The bottommost panel shows you the "undo" delimiter.
In this example, the output of the history command shows you can invoke the undo command four times.
Notice that the list participants command is not shown in the "History" section as it does not change data.
Also note that the undo-able commands are numbered, with the 1st undo-able command being the most recently executed command (the EditParticipantCommand), and the 4th undo-able command being the oldest executed command. In this case, the maximum number of commands you can undo at once is 4.
Also note that in this case, no commands are redo-able, that’s why there are no panels between the "redo" and "current" delimiters. Hence, executing redo command will result in an error.
5.13. Undo Previous Commands: undo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_UNDO]
Undoes previously executed commands.
There are 2 ways for you to use this commands:
-
undo: This implicitly executesundo 1and undoes 1 command only. -
undo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_UNDO]: This undoesNUM_COMMANDS_TO_UNDOcommands, subject to the number of available commands that you can undo, as per the output of thehistorycommand.
Format: undo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_UNDO]
5.14. Redo Previous Commands: redo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_REDO]
Redoes previously executed commands.
There are 2 ways for you to use this commands:
-
redo: This implicitly executesredo 1and redoes 1 command only. -
redo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_REDO]: This redoesNUM_COMMANDS_TO_REDOcommands, subject to the number of available commands that you can redo, as per the output of thehistorycommand.
Format: redo [NUM_COMMANDS_TO_REDO]
5.15. Command History Navigation
Navigate to previous commands by pressing the alt key Alt, together with the up ↑ or down ↓ arrow keys. For Mac users, press the option key Opt in place of the alt key Alt instead. Should you have re-mapped/re-purposed the alt key Alt, press the remapped key on your keyboard instead.
5.16. Scoring: score
The score command allows you to change a particular team’s score. It allows you to:
-
Add points to a team’s score
-
Subtract points from a team’s score
-
Set a team’s score to a certain number of points
-
Reset a team’s score
The usage of the above commands are explained in the following subsections.
5.16.1. Add points: score add TEAM_ID POINTS
Adds the value of POINTS to the current score of the team with ID TEAM_ID.
Format: score add TEAM_ID POINTS
Example:
-
score add T-1 20will add 20 points to the score of the team with ID T-1. -
score add T-5 60will add 60 points to the score of the team with ID T-5.
5.16.2. Subtract points: score sub TEAM_ID NEW_POINTS
Deducts the value of POINTS from the current score of the team with ID TEAM_ID.
Format: score sub TEAM_ID POINTS
Example:
-
score sub T-1 15will subtract 15 points from the score of the team with ID T-1. -
score sub T-5 10will subtract 10 points from the score of the team with ID T-5.
5.16.3. Set points: score set TEAM_ID NEW_POINTS
Sets the score of the team with ID TEAM_ID to a new score NEW_POINTS, regardless of the team’s current score.
Format: score set TEAM_ID POINTS
Example:
-
score set T-1 15will set the score of the team with ID T-1 as 15. -
score set T-5 10will set the score of the team with ID T-5 as 10.
5.16.4. Reset points: score reset TEAM_ID
Resets the score of the team with ID TEAM_ID to the minimum amount of points allowed, which is set to 0 as default.
Format: score reset TEAM_ID
Example:
-
score reset T-1will reset the score of the team with ID T-1. -
score reset T-5will reset the score of the team with ID T-5.
5.17. Team Rankings: leaderboard and getTop k
In addition to assigning scores to teams, Alfred also facilitates viewing the leaderboard and fetching the top teams in the hackathon with ease. The following subsections explain how to do so within Alfred.
5.17.1. View Leaderboard: leaderboard
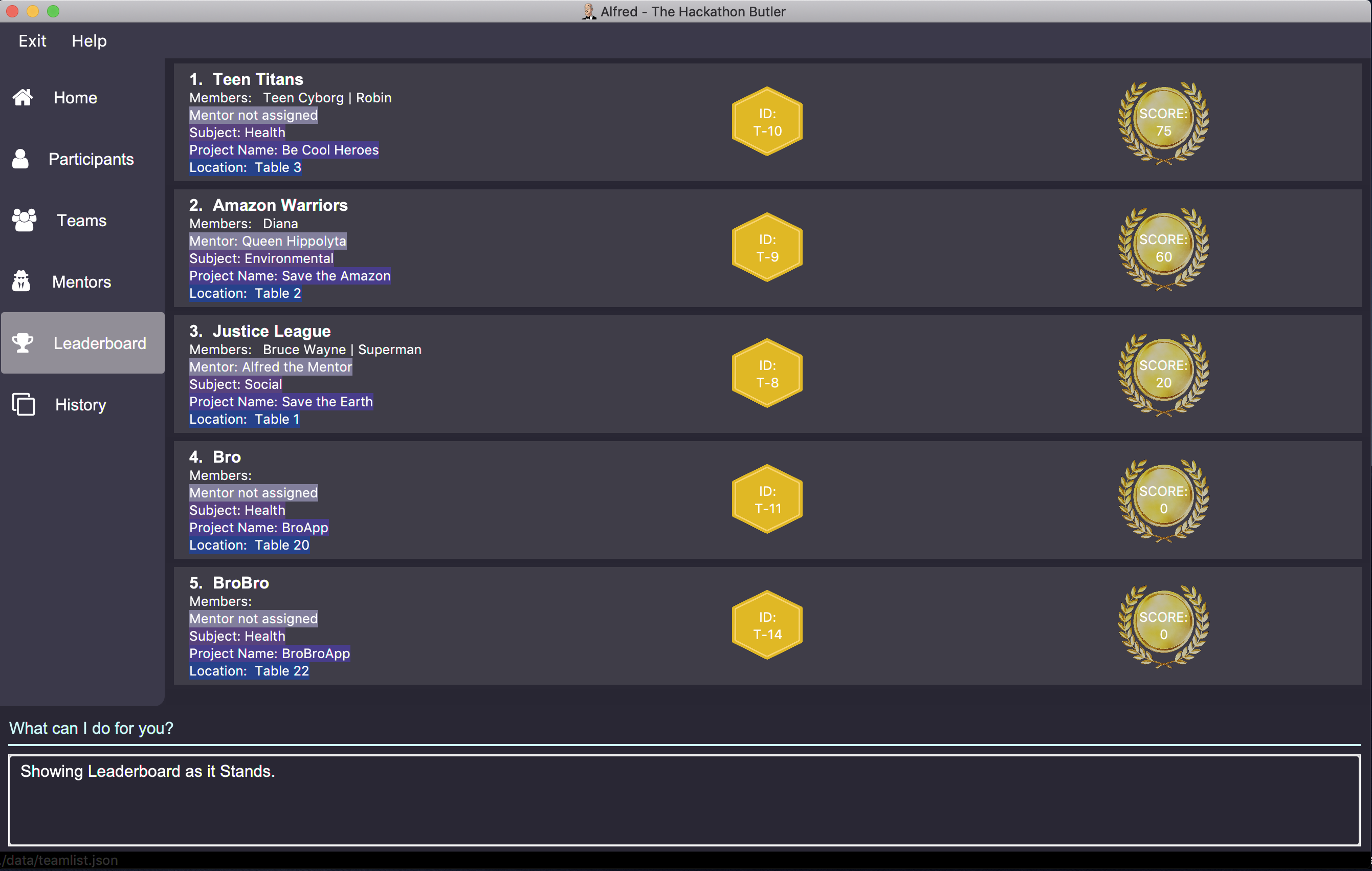
Displays the ranking of all the teams in the hackathon in descending order of their points.
Format: leaderboard
Running leaderboard will show the following on the GUI:
5.17.2. Get the top k teams: getTop K
Lists the top k teams in the leaderboard, where k is a valid positive integer which you specify.
Format: getTop K
Example:
-
getTop 2will display the top 2 teams with the highest points in the hackathon as shown below:
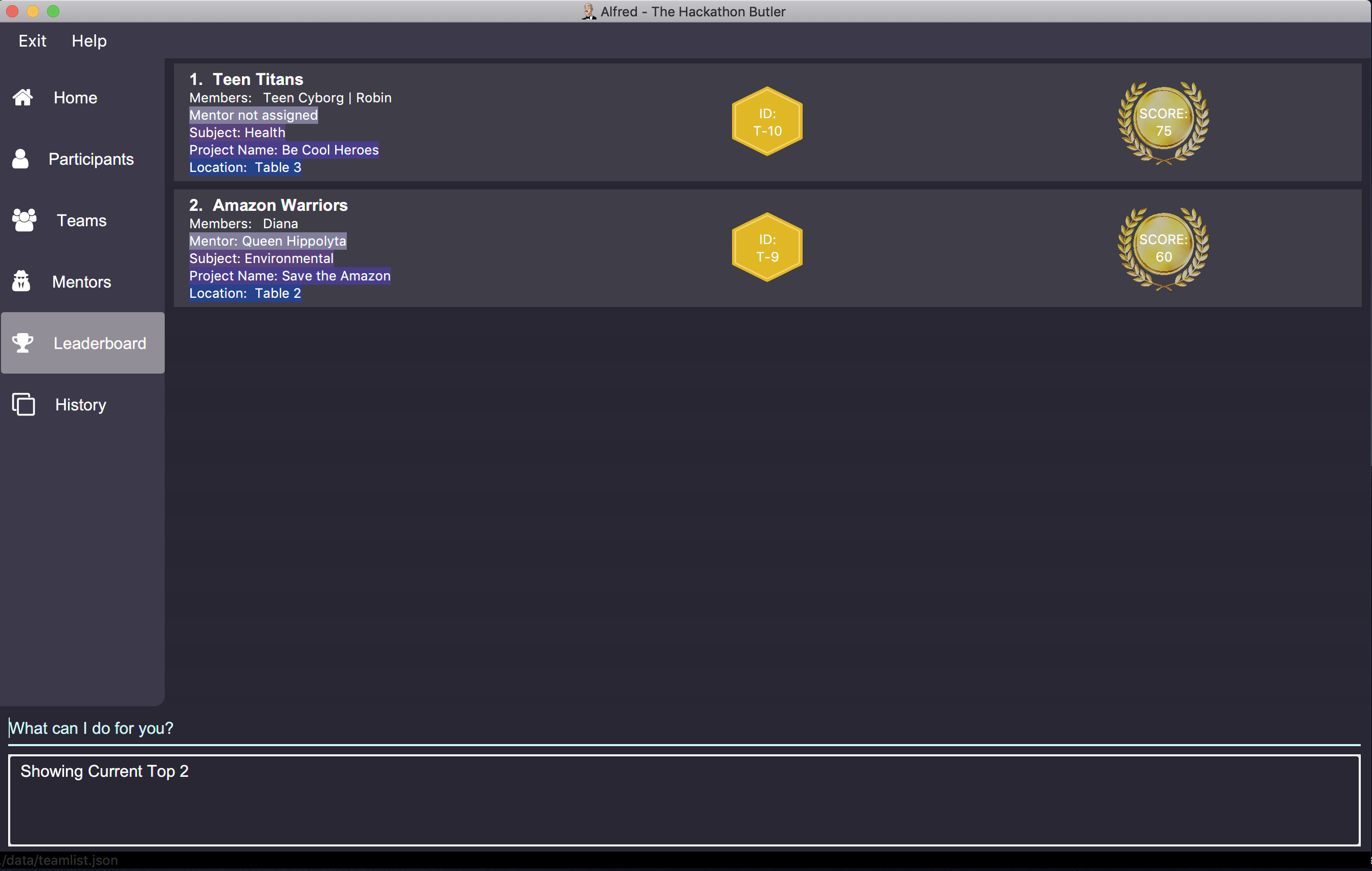
-
getTop 4will display the top 4 teams with the highest points in the hackathon as shown below:
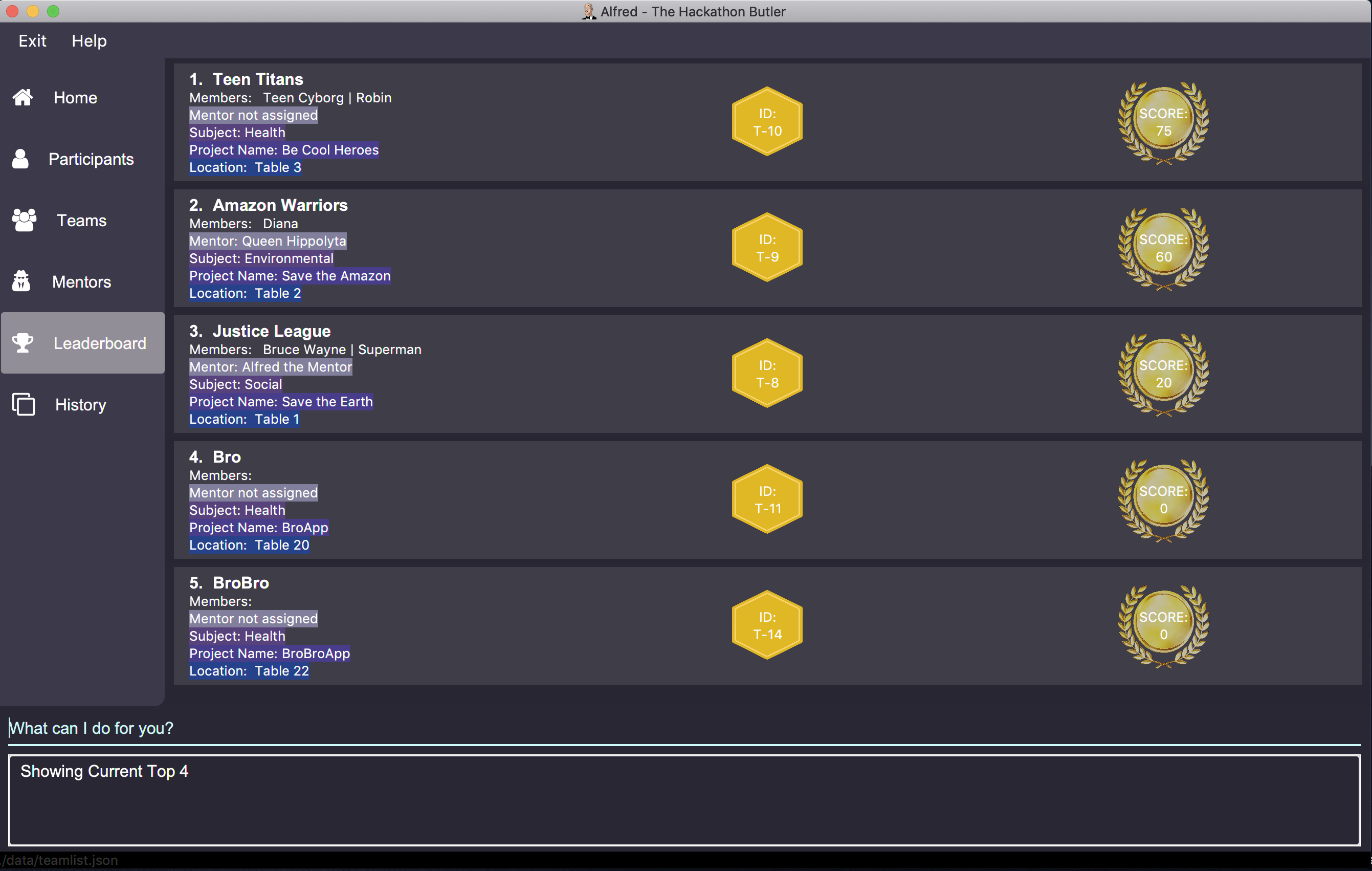
Note that due to the tie between the fourth and fifth teams, more than 4 teams are shown.
5.17.3. Extensions to leaderboard and getTop K Command
To provide additional functionalities to the leaderboard and getTop k commands, there are few extensions that can be added to these two commands to allow you to customize them to your needs. These extensions are explored below.
5.17.3.1. Tie-Break
By default Alfred leaderboard and getTop k commands fetch and display teams in descending order of their score, and by the order they were added into Alfred in case of tied scores.
Alfred’s tiebreak feature provides an extension to the leaderboard and getTop k commands allowing you to choose how you want to break the tie between the teams when calling these commands. To break a tie, follow the following format:
-
leaderboard tb/METHOD_1 METHOD_2 METHOD_3in the case of aleaderboardcommand -
getTop NUMBER tb/METHOD_1 METHOD_2 METHOD_3in the case of agetTop NUMBERcommand
where METHOD_N is one of the following currently available tie-break methods:
-
moreParticipants: teams with more participants are win the tie. -
lessParticipants: teams with lesser participants are win the tie. -
higherId: teams registered more recently (hence the highest ID) win the tie. -
lowerId: teams registered earlier (hence the lowest ID) win the tie. -
random: in case all methods used yield no distinct winner,randomcan be used as a method of last resort to break a tie in favour of a randomly chosen team.
Example:
-
leaderboard tb/moreParticipants lowerIdwill display the leaderboard on the UI with Alfred breaking the tie between teams with equals scores based on which team has more participants, and if the number of participants is equal then by which team has the lower ID.
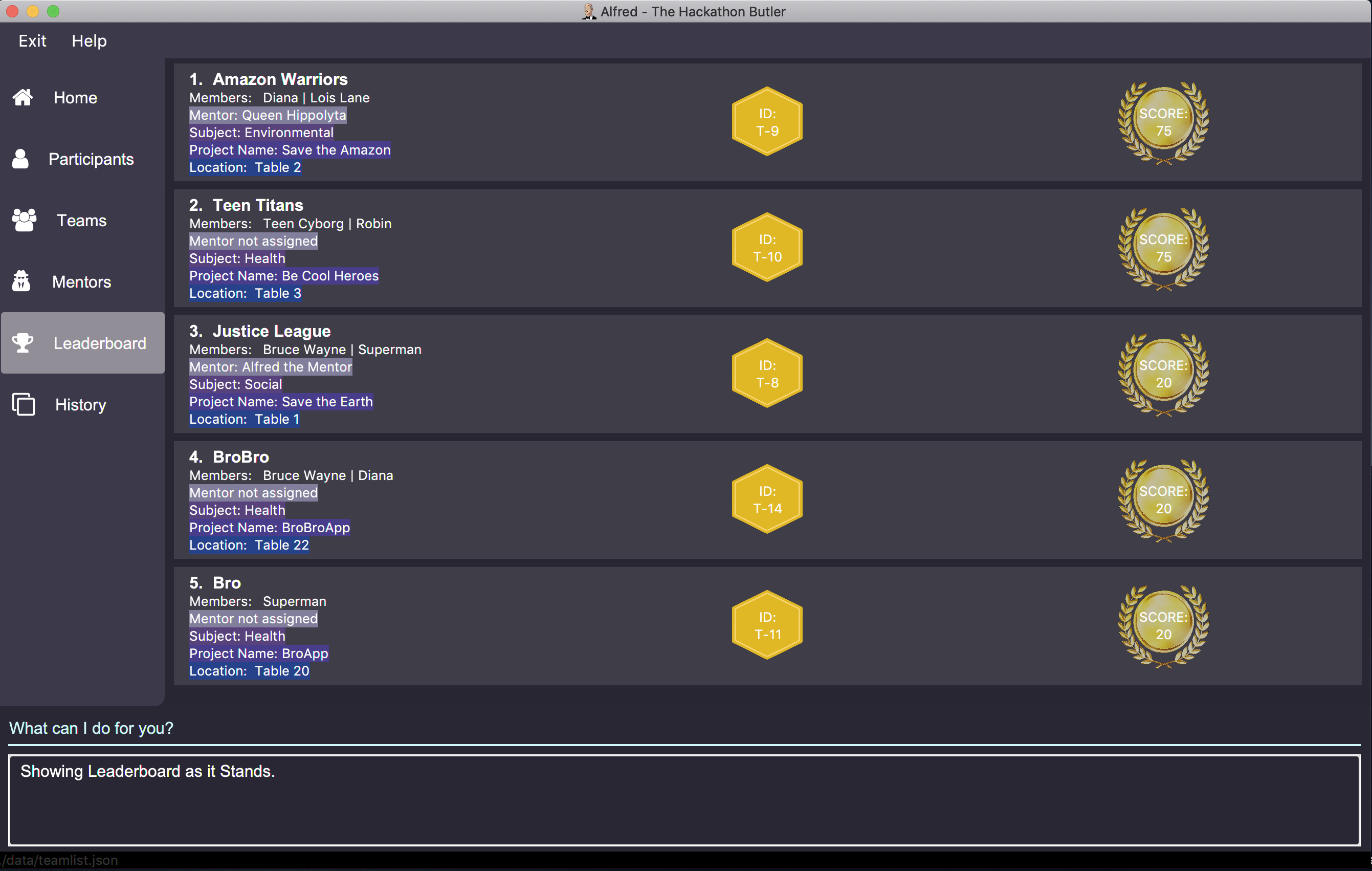
Note that in the above team "BroBro" comes above team "Bro" despite having the same number of points as "BroBro" has more participants. Secondly, "Amazon Warriors" comes first before "Teen Titans" despite having the same score and number of participants, since "Amazon Warriors" has a lower ID.
-
getTop 3 tb/lessParticipants randomwill display the top 3 teams on the UI with Alfred breaking the tie between teams with equals scores based on which team has fewer participants, and if the number of participants is equal then Alfred will randomly pick the winners for the tie.
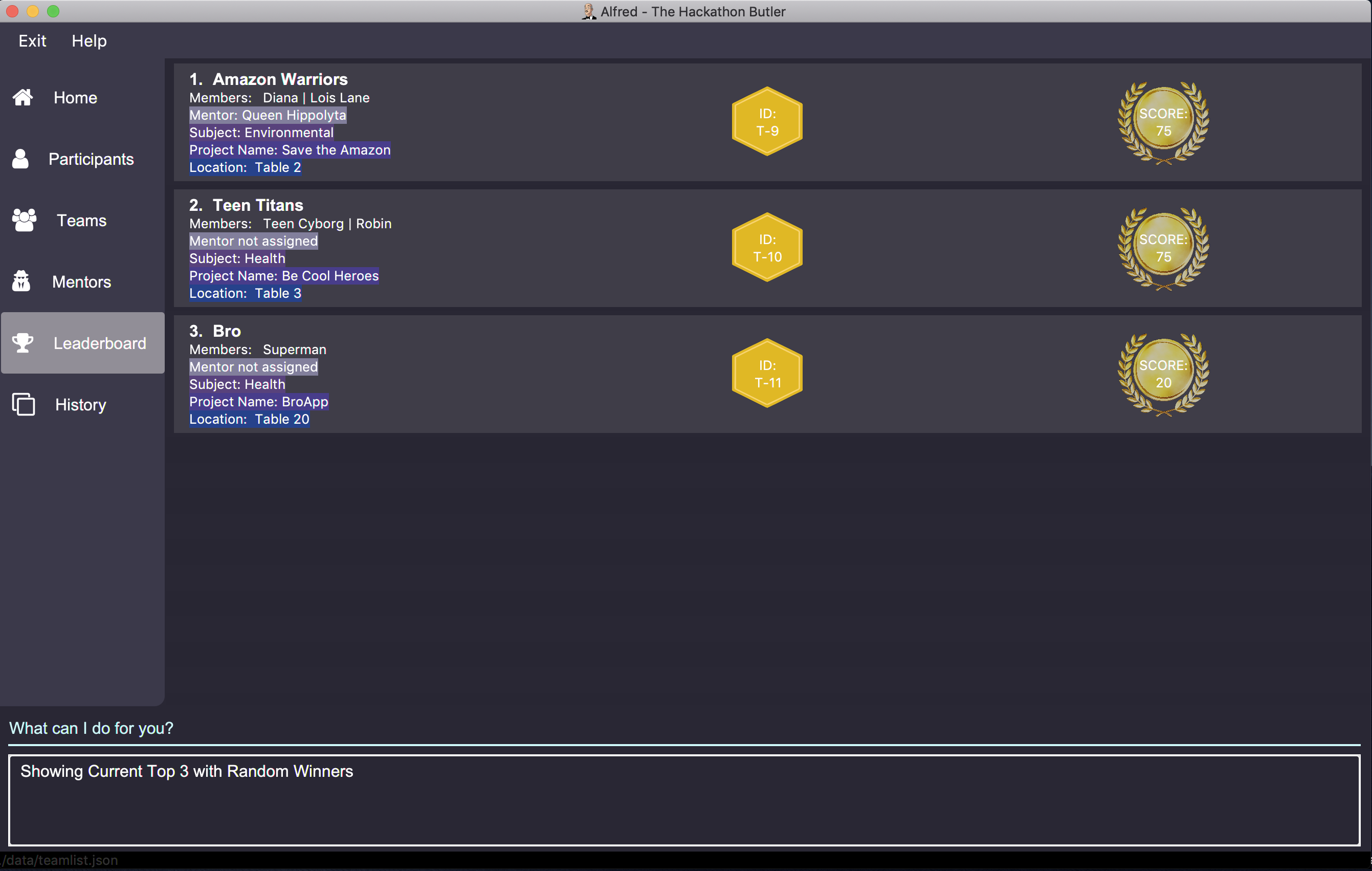
Note that in the above "Amazon Warriors" comes first before "Teen Titans" despite having the same score and number of participants, due to the random tiebreak. Repeating the above command would change the outcome due to the random nature of the tiebreak.
5.17.3.2. Filter by Subject
By default, when running either the leaderboard or getTop k command, Alfred will show all the appropriate teams irrespective of their subject. However, Alfred’s filter by subject feature provides the ability to view the leaderboard or top teams for a specific subject, by following the below format:
-
leaderboard s/SUBJECT_NAMEin the case of aleaderboardcommand -
getTop k s/SUBJECT_NAMEin the case of agetTop kcommand
Example:
-
leaderboard s/Healthwill display the leaderboard consisting only of teams with the subject "Health" as shown below:
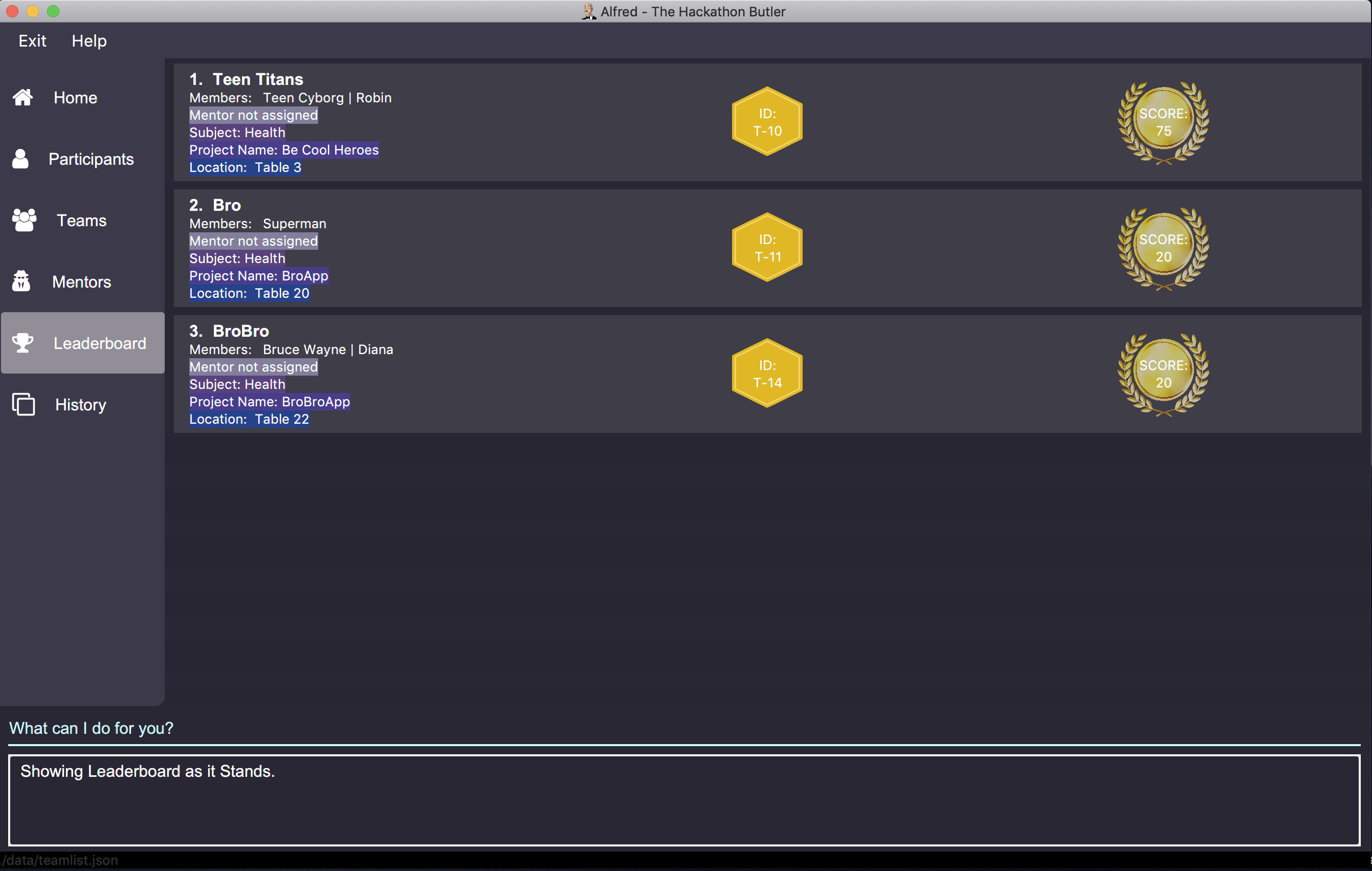
-
getTop 3 tb/moreParticipants s/Healthwill display the top 3 teams within the hackathon, all of which will consist of only of those with subject "Health". Additionally, any ties between these teams will be broken using the tiebreak method "moreParticipants" - the team with more participants wins the tie.
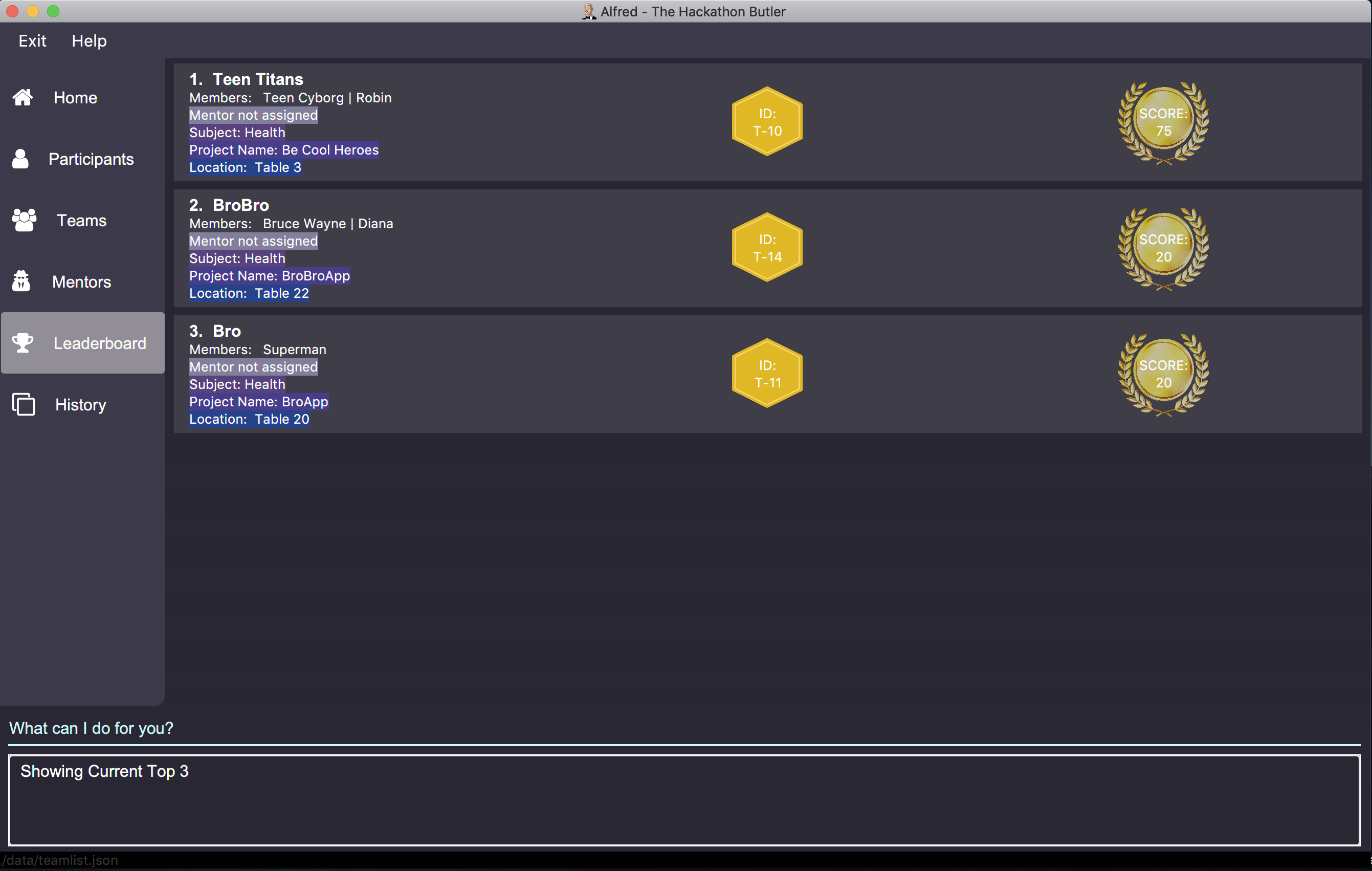
Note that in the above team "BroBro" goes above team "Bro" as it has more participants, despite both teams having equal scores.
5.18. Bulk Registration: import fp/PATH_TO_CSV_FILE [fp/PATH_TO_ERROR_FILE]
You may import multiple entities at once into Alfred through the specification of a CSV file.
If the PATH_TO_ERROR_FILE is specified, Alfred will create a new CSV file with all of the lines that were not able to be loaded.
Example:
-
import fp/C:/User/Hackathon2019/participant.csvwill import data from the participant.csv file into Alfred. -
import fp/Hackathon2019/participant.csvwill look for the CSV file in your current directory (or the folder where alfred.jar is downloaded).
|
First, locate the desired file in your respective file manager. On Windows, hold down shift, click the file, then click Copy as path to copy its file path.On Mac, right-click the file, hold down OPTION key, then click Copy (item name) as Pathname to copy its file path.
|
Example usage of error file is shown below.
5.18.1. CSV File Formatting
In order for the contents of the CSV file to be correctly loaded into Alfred, the file has to be in the correct format, which will be discussed below. For most platforms, there will be a default editor for a CSV file. If the editor is anything other than text editor, please ensure that the default separator is set as one comma (,). There may be whitespaces surrounding a comma if it is easier for you to edit.
5.18.1.1. Mentor Data
Header: EntityType,ID,Name,Phone,Email,Organization,SubjectName
Example:
-
M,M-1,Alfred the Mentor,12345678,alfred@batcave.com,Batcave Corp.,Education
-
M,1,Alfred the Mentor,+6512345678,alfred@batcave.com,Batcave Corp.,EDUCATION
-
M,,Alfred the Mentor,+65 12345678,alfred@batcave.com,Batcave Corp.,Education
5.18.1.2. Participant Data
Header: EntityType,ID,Name,Phone,Email
Example:
-
P,P-1,Bruce Wayne,23456789,wbruce@wayne.ent
-
P,1,Bruce Wayne,+6523456789,wbruce@wayne.ent
-
P,,Bruce Wayne,+65 23456789,wbruce@wayne.ent
5.18.1.3. Team Data
Header: EntityType,ID,Name,Participants,Mentor,SubjectName,Score,ProjectName,Location
Example:
-
T,T-1,Justice League,,,Social,100,Save the Earth,1
-
T,1,Justice League,[P-1|P-2|P-3],M-1,Social,100,Save the Earth,1
-
T,,Justice League,[P-1|P-2|P-3],1,Social,100,Save the Earth,1
Alfred will recognize each of the entity headers and will not count it as an error. Example CSV file may look like this:
Alfred.csv
EntityType,ID,Name,Participants,Mentor,SubjectName,Score,ProjectName,Location
T,,Justice League,[P-1|P-2],M-1,Social,100,Save the Earth,1
T,,Amazon Warriors,[P-3|P-4],,Environmental,100,Save the Amazon,2
EntityType,ID,Name,Phone,Email,Organization,SubjectName
M,1,Alfred the Mentor,+6512345678,alfred@batcave.com,Batcave Corp.,EDUCATION
M,,Joker,,is this my email??
EntityType,ID,Name,Phone,Email
P,1,Bruce Wayne,+65 23456789,wbruce@wayne.ent
P,2,Superman,+6519231486,ckent@dailyplanet.org
P,3,Diana,+6547234328,diana@amazon.com
P,3,Lois Lane,+6598765432,loislane@dailyplanet.org
You can also download a sample CSV file here to try it out for yourself.
Assuming Alfred has no data, we can see that lines 3, 6, and 11 will fail.
-
Line 3: No participant with ID P-4 exist (Missing entity)
-
Line 6: Phone number is missing and email is invalid (Invalid format)
-
Line 11: Another participant with ID P-3 exists (Duplicate entity)
If you give the following command to Alfred,
import fp/Alfred.csv fp/Alfred_Errors.csv
then the following CSV file will be created where Alfred.csv is located at.
Alfred_Errors.csv
T,,Amazon Warriors,[P-3|P-4],,Environmental,100,Save the Amazon,2
M,,Joker,,is this my email??
P,3,Lois Lane,+6598765432,loislane@dailyplanet.org
5.19. Export Data: export [{mentor/participant/team}] [fp/DESIRED_CSV_FILE_PATH]
You may export Alfred data to an external CSV file. If the entity type is specified, Alfred will export all the data corresponding to that entity type only. If the desired CSV file path is left empty, Alfred will create a CSV file at the default location (./AlfredData/Alfred_Data.csv).
Example:
-
exportwill export all entities' data in Alfred to the default file path:/AlfredData/Alfred_Data.csv. -
export mentor fp/data/Alfred.csvwill export all mentor data in Alfred to/data/Alfred.csv. If the any folders do not happen to exist, Alfred will create them for you.
5.20. Help command
The help command will list all the commands you need to use this application properly!
Simply run help.
If you want the help window to close, simply run another command that is not help and the window
will close by itself.
5.21. Home command: home
This command allows you to navigate to the homepage where the system statistics are updated in real time. The homepage statistics are also available when you start-up the application.
Example: Suppose you want to check the distribution of teams by subjects, in order to gauge the demand for mentors for each subject.
Instead of manually sieving through all the teams by the subject that their project is on, you can easily view the distribution of teams and mentors by subject via the home command.
To navigate to home:
-
Type home into the command box, and press
Enter -
The result box will display the message “Showing homepage” in the result box. You can see the statistics and the ‘Home’ section of sidebar being highlighted. Below is the layout of the homepage:
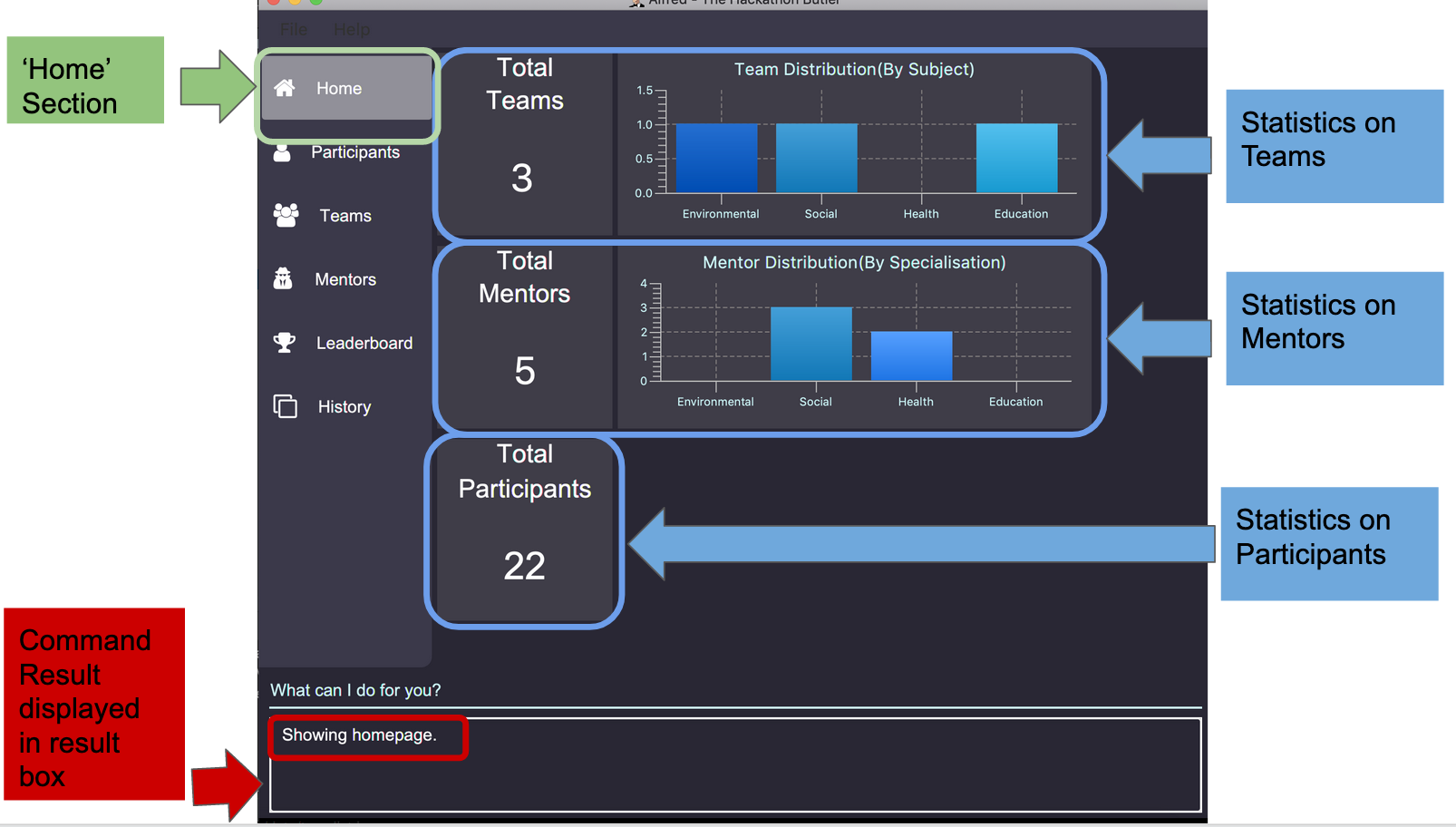
home command5.22. Command Suggestion Prompt
As you type, there will be a popup box predicting the type of commands you are going to type. You can navigate through these suggestions and choose the template that suits you.
Example:
Let us suppose that you want to type the command add mentor and you forgot the fields that are required in the command.
Instead of going through the user guide to look for the command, a popup box will appear as you type. The content in this box will change as you type, such that the commands suggested will start with the words or letters that you have already entered.
As you type:
-
Type ‘add’ into the command box, and
add participant,add mentorandadd teamcommands will be suggested to you. The grey text are meant as guides and blue text are meant as usage instructions . These text will not appear when you choose the command of choice.
-
Press the up arrow or down arrow arrow keys to navigate up and down the popup box.
-
Press Enter to choose the command of your choice. The command will then appear on the user input box.
-
Press left arrow or right arrow keys to navigate the cursor and fill in the respective fields. Press Enter to execute the command.
5.23. Seating: locate {PARTICIPANT/TEAM} (Coming in v2.0)
Find where a particular participant or team is seated.
Examples:
-
locate n/Brianwill tell you where the participant Brian is seated. -
locate n/GenericTeamNamewill tell you where the team GenericTeamName is seated.
5.24. Swag (Coming in v2.0)
5.24.1. Add Swag: add swag DESCRIPTION QUANTITY
Add swag to inventory
Examples: add swag Android Plushie 5
5.24.2. Track inventory of available swags: list swag
List the currently available swag
5.25. Schedule (Coming in v2.0)
5.25.1. Add schedule: addSchedule TIME TEAM_ID MENTOR_ID
Add a schedule for a team
5.25.2. Update schedule: updateSchedule SCHEDULE_ID TIME TEAM_ID MENTOR_ID
Update a schedule for a team
5.25.3. Delete schedule: deleteSchedule SCHEDULE_ID
Delete a Schedule for a Team
5.26. Food (Coming in v2.0)
5.26.1. Add Food Company and Inventory: addFoodCompany COMPANY_NAME INVENTORY QUANTITY
Add a Food Company and it associated food item inventory
5.26.2. Mark Food as Received: receiveFood COMPANY_NAME INVENTORY QUANTITY
Mark the inventory as received
5.26.3. List Food Inventory: list food
List the food inventory and its current status (e.g. delivering, received)
5.27. Waitlist (Coming in v2.0)
5.27.1. Add to waitlist: addToWaitList PARTICIPANT_ID
Add a participant to a waitlist when the number of participants exceeds a stipulated capacity.
5.27.2. Remove from waitlist: removeFromWaitList PARTICIPANT_ID
Remove a participant from the waitlist.
5.27.3. List by Registration Time: listWaitList
Go through the waitlist and list the participants in the waitlist in ascending orger of registration time.
6. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: First, download alfred.jar in your other computer. Then, transfer the data folder at where alfred.jar is downloaded in your old computer over to your new computer. In your new computer, transfer the data folder over to where alfred.jar is downloaded.
7. Command Summary
| Command | Function | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Add an Entity |
Add an Entity for Alfred to keep track |
|
Participant: |
Update an Entity |
Edits an entity based on the supplied parameter values |
|
Participant: |
List all Entities |
Shows a list of all the entities corresponding to the entity type |
|
Participant: |
Deleting an Entity |
Deletes an Entity, so that Alfred will no longer keep track of that Entity |
|
Participant: |
Finding an Entity |
Searches for Entities by their name |
|
Participant: |
List Undo/Redo-able Commands |
Displays the Undo/Redo-able Commands in the "History" section of the GUI |
|
|
Undo Previous Command |
Undoes the previously executed command. Look at output of |
|
|
Redo Next Command |
Redoes the next command. Look at output of |
|
|
List Team Rankings |
Displays the ranking of the teams in the Hackathon in descending order of their points |
|
Team: |
List Team Rankings with Tie Break |
Displays the ranking of the teams in the Hackathon in descending order of their points with specified tiebreak methods used to break ties |
|
Team: |
Get the top k teams |
List the top k teams in the leaderboard, where k is a number (NUMBER) which you specify |
|
Team: |
Get the top k teams with Tie Break |
List the top k teams in the leaderboard with specified tiebreak methods used to break ties, where k is a number (NUMBER) which you specify |
|
Team: |
Add points to a Team |
Adds the value of POINTS to the current score of the team with TEAM_ID |
|
Team: |
Subtracts points from a Team |
Deducts the value of POINTS from the current score of the team with TEAM_ID |
|
Team: |
Sets points of a Team |
Sets the score of the team with TEAM_ID to a new score NEW_POINT |
|
Team: |
Bulk Registration |
Adds multiple participants at once into Alfred through the specification of a .csv file |
|
|
Export Data |
Exports all data in Alfred to an external CSV file |
|
All: |
Add a schedule for a Team (Coming in v2.0) |
Adds a time slot where the Team of TEAM_ID meets with Mentor of MENTOR_ID |
|
|
Update schedule of a Team (Coming in v2.0) |
Updates the existing schedule of SCHEDULE_ID of a Team of TEAM_ID. New schedule will be added if the Team does not have an existing schedule of SCHEDULE_ID |
|
|
Delete a schedule for a Team (Coming in v2.0) |
Deletes a time slot where the of SCHEDULE_ID |
|
|
Add addFoodCompany and Inventory (Coming in v2.0) |
Adds a Food with COMPANY_NAME, INVENTORY_QUANTITY and CATERING_TIME |
|
|
Marked Food as received (Coming in v2.0) |
Marks a Food with COMPANY_NAME and CATERING_TIME as received |
|
|
List all Food (Coming in v2.0) |
Lists the inventory of Food |
|
|
Add User to WaitList (Coming in v2.0) |
Adds a prospective Participant by USER_ID to Waitlist |
|
|
Remove a User from WaitList (Coming in v2.0) |
Removes a prospective Participant by USER_ID from Waitlist |
|
|
List all User in WaitList (Coming in v2.0) |
Lists all prospective Participant in Waitlist |
|
|